Calculation of work function of K/Cu (001) via ESM method#
Effective Screening Medium (ESM) method1 is an efficient and elaborate method to calculate electronic state of surface or interface under two-dimensional periodic boundary condition. ESM method can treat such surface models as are applied electric field and electrically polarized with accuracy.
We calculated work function of K/Cu (001) via ESM method on Advance/NanoLabo.
Setting up of ESM calculation#
You can execute ESM calculation easily just by activating ESM method and selecting boundary condition along Z direction on Advance/NanoLabo. We selected vacuum/slab/vacuum boundary condition along Z direction to calculate work function.
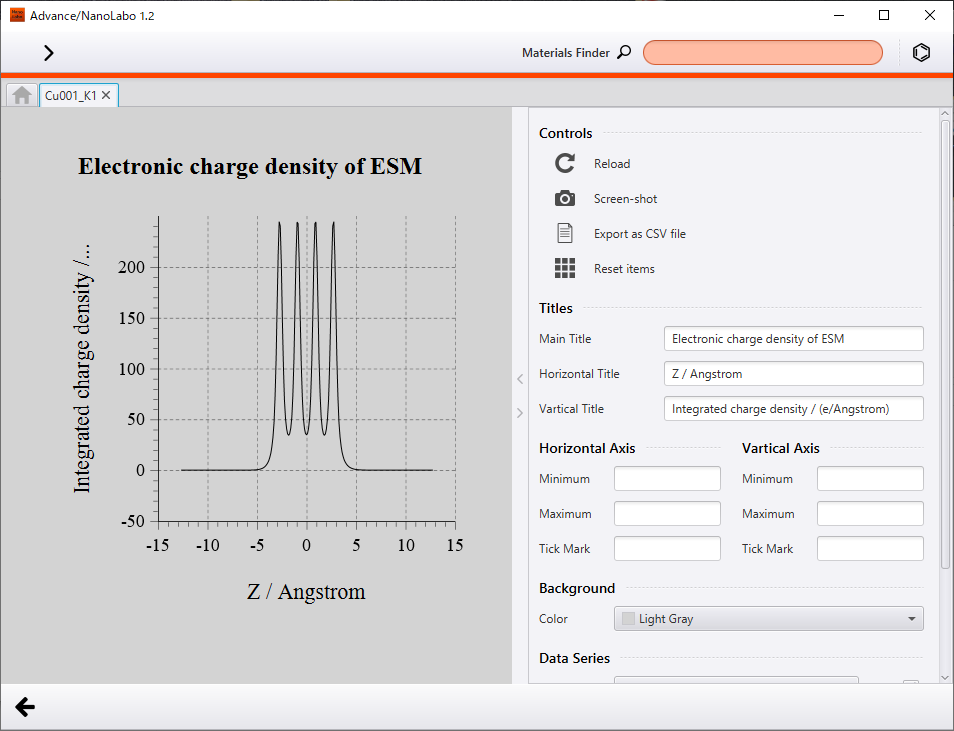
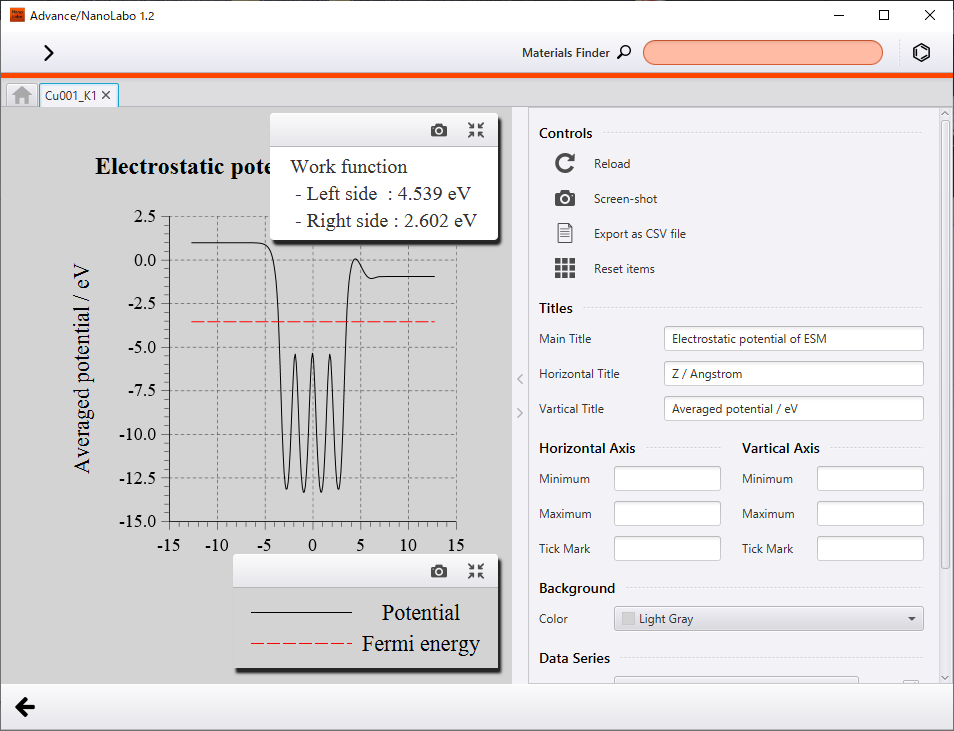
We show calculated electric charge density distribution and electrostatic potential along Z direction, which has information of work function.
Work function of K/Cu (001) was obtained as 2.60 eV and that of Cu (001) was obtained as 4.64 eV. We can see from these results that adsorption of a K atom reduces work function of Cu (001) surface by about 2 eV.
K coverage dependence of work function#
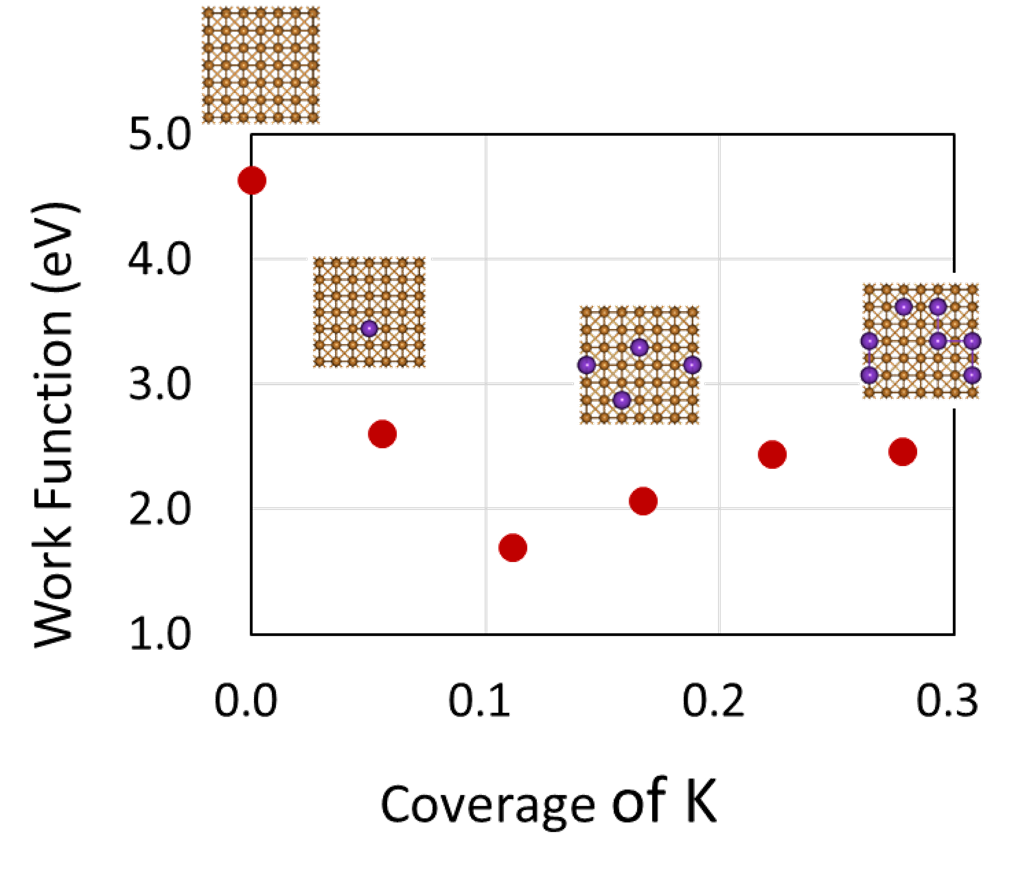
We executed similar calculations for K/Cu (001) systems with different K coverage to investigate K coverage dependence of work function. We show the result graph, in which the horizontal axis corresponds to coverage of K2 and the vertical axis corresponds to work function.
At first work function decreases sharply with increasing K coverage, and then it converges to a constant value after a local minimum point.
Such a characteristic coverage dependence of work function has been observed experimentally3.
It is said that the sharp decrease of work function for low coverage is caused by surface dipole moments increased by ionized K atoms. Also, it is considered that K ions turn back into electrically natural with increasing coverage further and then the effect of the surface dipole moments is reduced4.
関連ページ#
- ナノ材料解析統合GUI Advance/NanoLabo
- 解析分野:ナノ・バイオ
- 産業分野:材料・化学
- Advance/NanoLabo Product Information
- Advance/NanoLabo Documentation
-
Calculation solver supporting ESM method is Quantum Espresso. ↩
-
Coverage of K = Number of adsorbed K atoms/ Number of surface Cu atoms ↩
-
T. Aruga, et al.: "Valence-electronic structure of potassium adsorbed on Cu(001) deduced from work-function change and electron-energy-loss spectroscopy" Phys. Rev. B 34(1986) 8237 ↩
-
Murata, Y.: "Surface Physics (Asakura Physics System)" Asakura Publishing (2003) Published in Japanese. ↩