Crystallization of supercooled water by applying electric field in molecular dynamics simulation#
We introduce molecular dynamics simulation of water under external electric field with Advance/NanoLabo, an integrated GUI for nanomaterials.
We simulated how supercooled water molecules orient under external static electric field and crystallize into cubic ice.
The entire process from modeling to running calculation and analysis of results was executed on Advance/NanoLabo.
Generation of a calculation model and setting of calculation schemes#
We generated a model which contains 256 water molecules with packing molecules function.Its cell size is 20 Å×20 Å×20 Å and its density is 0.96 g/cm3. We employed NVT ensemble, in which volume and temperature are constant, as statistical ensemble.
We adopted TIP3P as water model. You can assign TIP3P force field parameters to water molecules just by selecting OPLS-AA force field and clicking Apply button on Advance/NanoLabo.
We equilibrated the system at 298 K for 200 ps and then decreased temperature to 250 K at a constant rate for 200 ps. We equilibrated the resulting configuration for a further 200 ps at 250 K and then applied external electric field of 0.5 V/Å along Z direction for 600 ps. We also executed similar simulation without applying electric field for comparison. In these simulations, we set simulation time step as 0.5 fs.
You can set how electric field is applied to calculation schemes on Option screen of Advance/NanoLabo.
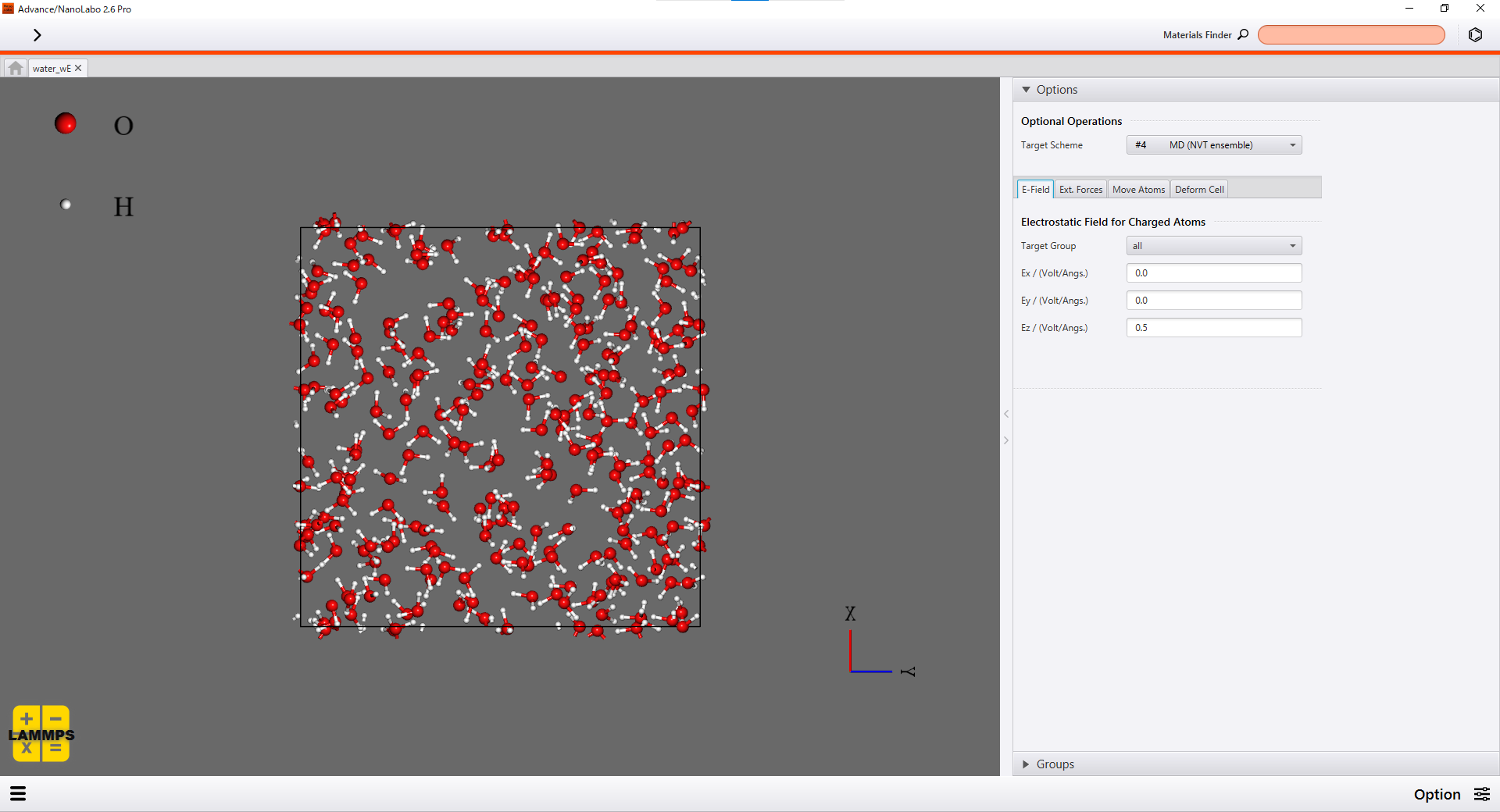
|
Setting of electric field on Option screen |
Analysis results#
We show oxygen–oxygen radial distribution function (RDF) G(r) obtained from the simulations below. We can see that water molecules under electric field exhibit long-range order compared to those without electric field from the RDFs. These results indicate that supercooled water crystallize by applying electric field1.
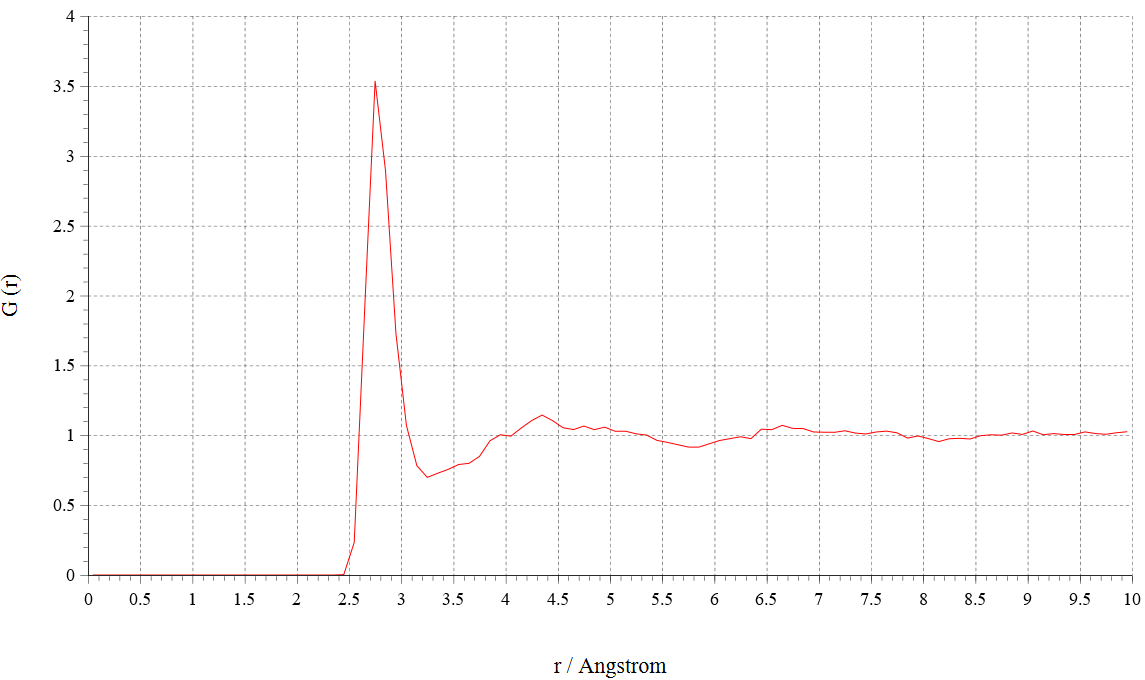
|
RDF(E=0.0 V/Å) |
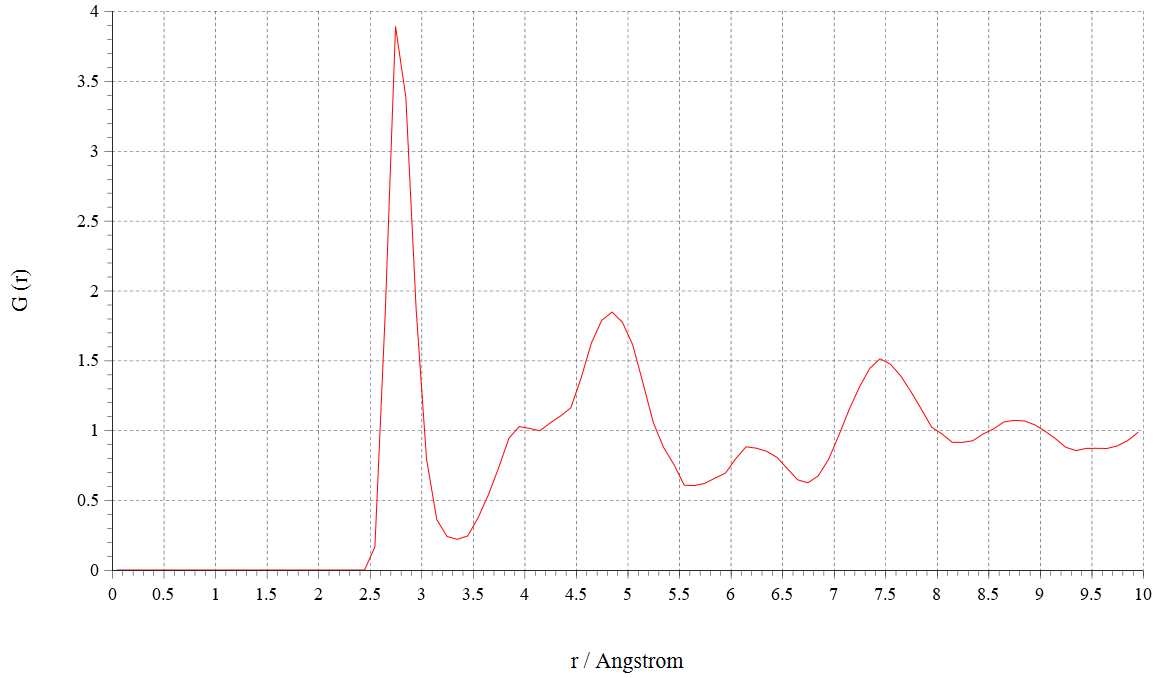
|
RDF(E=0.5 V/Å) |
On Advance/NanoLabo, you can calculate and visualize RDFs just by turning on Radial Distribution button.
Tips
You can change the calculation range of RDFs from 5 Å(default) to 10 Å by entering "compute RDF all rdf 100 1 1 1 2 2 2 cutoff 10"2 on User's screen.
As shown below, water molecules of the final structure under electric field aligns regularly as compared with those without electric field.
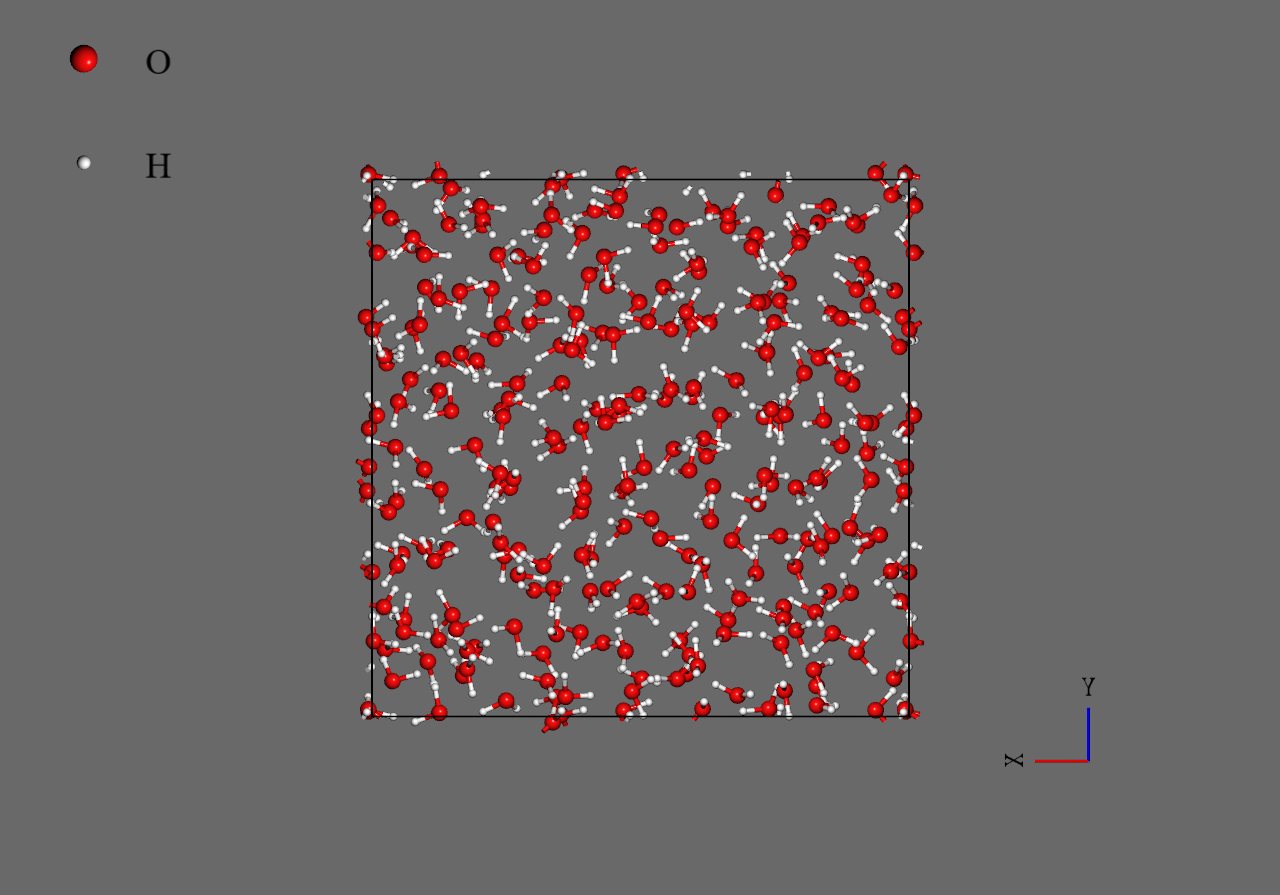
|
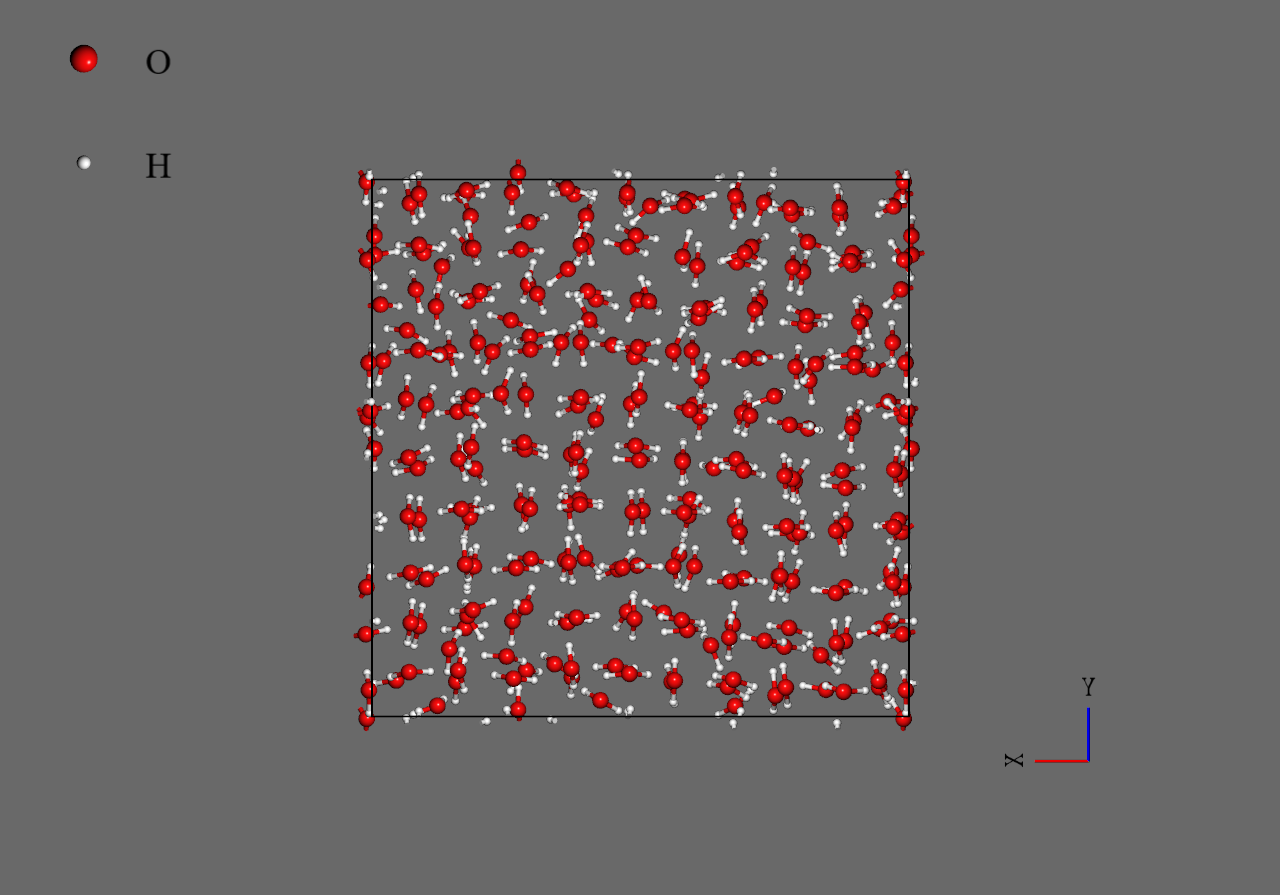
|
Final structure (E=0.0 V/Å) |
Final structure (E=0.5 V/Å) |
We also show a part of the final structure under electric field below. We can see that water molecules exhibit hydrogen-ordered cubic ice structure3.
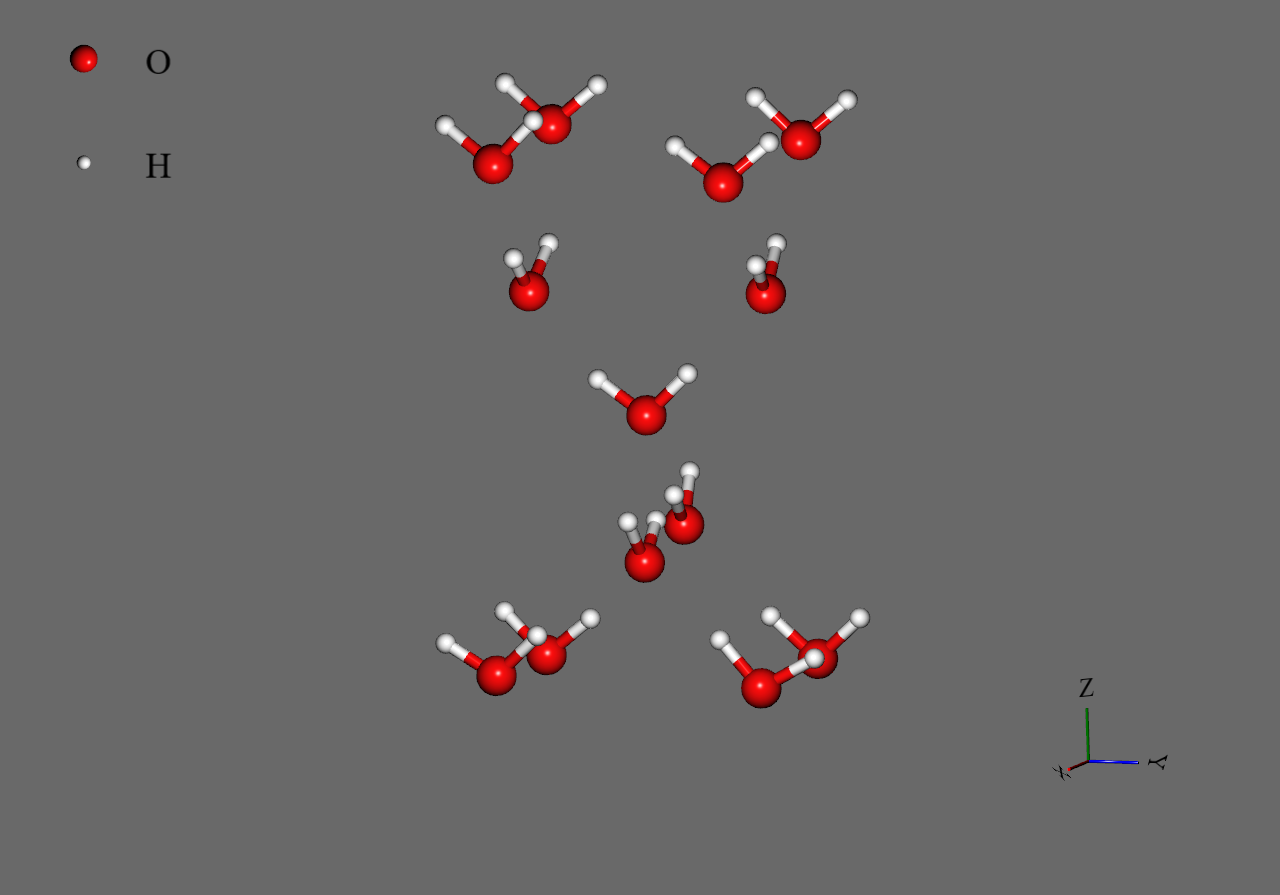
|
Hydrogen-ordered cubic ice structure |
関連ページ#
- ナノ材料解析統合GUI Advance/NanoLabo
- 解析分野:ナノ・バイオ
- 産業分野:材料・化学
- Advance/NanoLabo Product Information
- Advance/NanoLabo Documentation
-
SVISHCHEV, Igor M.; KUSALIK, Pater G. Crystallization of liquid water in a molecular dynamics simulation. Physical review letters, 1994, 73.7: 975. ↩
-
GEIGER, Philipp, et al. Proton ordering of cubic ice Ic: Spectroscopy and computer simulations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118.20: 10989-10997. ↩